When it comes to suspension parts, Johnny joint, Heim joint, and builder bushing are three commonly used components, but they differ greatly in terms of structure, materials, function, and ideal use cases. Here’s a quick overview of each, highlighting the best scenarios for each type.
- Johnny Joint: Known for its rebuildable design and high flexibility, the Johnny joint is ideal for off-road vehicles that need both strength and articulation, making it perfect for harsh terrain and heavy-duty applications.
- Heim Joint: Built for precision and durability, Heim joints are commonly used in high-performance racing and off-road builds where strength and flexibility are key, but vibration dampening is not a priority.
- Builder Bushing: Offering excellent vibration dampening, builder bushings are the best choice for vehicles that need a comfortable ride on both highway and off-road conditions, though they may not be as durable under extreme off-road use.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the differences between these three types of suspension parts.
Structural Comparison
Johnny Joint
Below are two disassembly diagrams of a Johnny Joint.


A Johnny joint is composed of a housing, bushing, ball, snap ring, and rod. The housing typically features a grease zerk for lubrication, and the ball usually comes with a high misalignment spacer. The rod is generally threaded with male threads; if female threads are required, customers typically purchase only the joint portion (everything except the rod) and weld the rod themselves.
Heim Joint
Below are two disassembly diagrams of a Heim Joint.

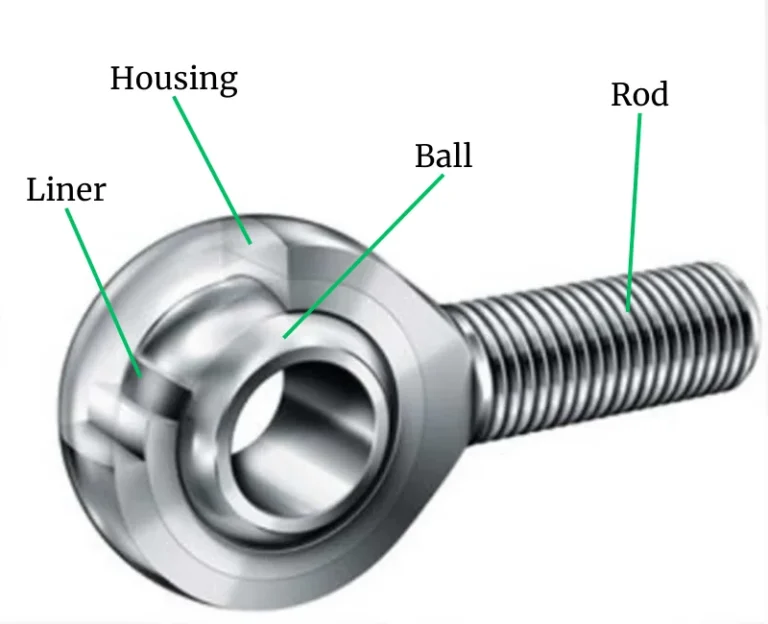
A Heim joint consists of a housing, ball, liner, and rod. Some Heim joints, especially those used in industrial applications, feature a grease zerk on the housing. The ball typically does not come with a misalignment spacer, which must be purchased separately. The rod can have either male or female threads, offering flexibility depending on the application.
Builder Bushing
Below are two disassembly diagrams of a builder bushing.
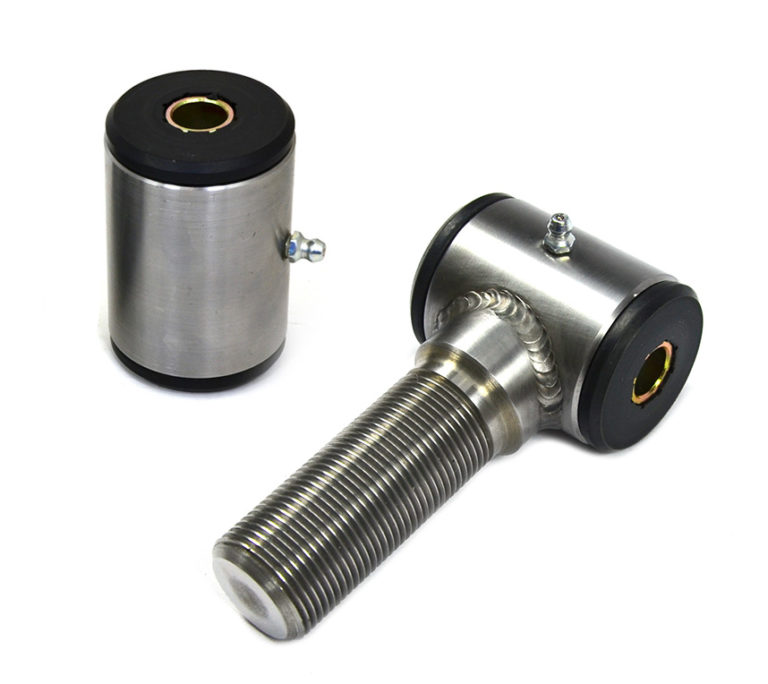


A builder bushing is made up of a housing, elastomer, and an inner sleeve. Some housings are equipped with a grease zerk for easier lubrication, while others may not have this feature.
Material Comparison
Johnny Joint
- Housing: Typically made from forged steel, 4130 chromoly steel, and stainless steel, providing strength and durability for heavy-duty applications.
- Ball: The ball is usually constructed from heat-treated steel, high carbon heat-treated steel, 52100 bearing steel, or 4130 chromoly steel, ensuring high performance and resistance to wear under heavy load.
- Bushing: Often made from High-Density Polyurethane or Delrin® (Acetal/POM), offering a combination of durability and flexibility for better articulation and impact absorption.
Heim Joint
- Housing: Made from 4130 chromoly steel, 7075-T6 aircraft aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon steel, providing strong structural integrity and lightweight options.
- Ball: Typically crafted from 52100 bearing steel or 440C stainless steel, designed for maximum strength and longevity in extreme conditions.
- Liner: The liner is often made from PTFE (Teflon) or bronze, offering low friction and reducing wear over time.
Builder Bushing
- Housing and Inner Sleeve: Usually constructed from carbon steel (most common), 4130 chromoly steel, or stainless steel, ensuring strength and corrosion resistance.
- Elastomer: Made from rubber or polyurethane, these materials provide flexibility and vibration dampening for smoother rides.
Working Principle Comparison
Johnny Joint
The Johnny joint operates by allowing the ball inside the housing to rotate within tightly fitted, rebuildable polymer bushings. As the link moves, the metal ball tries to rotate inside the polymer bushings, providing both flexibility and high load capacity.
Key Features:
- Allows significant angular misalignment.
- Provides moderate elastic buffering.
- Can withstand extremely high loads.
Heim Joint
The Heim joint relies on a metal ball rotating within a low-friction liner, such as PTFE (Teflon), allowing multi-axial, high-angle freedom of movement for the link.
Key Features:
- Allows a wide range of multi-axial angular movement.
- Provides the most precise and direct suspension geometry control.
- No elastic buffering—vibrations and impacts are directly transmitted through the metal.
Builder Bushing
The builder bushing operates by using the elastomer (rubber or polyurethane) in the middle to absorb and buffer the movement of the link through twisting and stretching. The link rotates or slightly deflects around its central axis.
Key Features:
- Allows limited angular change in the link.
- Primarily absorbs vibrations and reduces noise.
| Feature | Johnny Joint | Heim Joint | Builder Bushing |
|---|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Ball rotates within rebuildable polymer bushings. | Metal ball rotates within low-friction liner (PTFE). | Elastomer absorbs movement through twisting and stretching. |
| Angular Misalignment | Allows significant angular misalignment. | Allows multi-axial angular movement. | Allows limited angular change. |
| Elastic Buffering | Provides moderate elastic buffering. | No elastic buffering. | Primarily absorbs vibrations and reduces noise. |
| Load Capacity | Can withstand extremely high loads. | High precision, good for suspension geometry control. | Low load capacity, mainly for comfort. |
Cost of Use Comparison
Johnny Joint
The Johnny joint has the highest purchase cost, with a market price typically ranging from $70 to $130 (based on the original Johnny Joint brand RockJock 4×4, formerly Currie Enterprises).
However, its maintenance cost over time is relatively low to moderate, thanks to its rebuildable design. When the joint wears out, there’s no need to replace the entire expensive metal housing and center ball. Instead, you usually only need to replace the relatively inexpensive polymer inner cups, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Heim Joint
The Heim joint has a moderate purchase cost, generally priced between $45 and $80.
In terms of maintenance, it carries the highest ongoing costs. This is due to the Heim joint’s vulnerability to rapid wear from external contaminants such as sand, dirt, and water, which can cause it to become loose and noisy. Frequent replacements are necessary, and when replacing, you must purchase the entire joint, leading to higher long-term costs.
Builder Bushing
The builder bushing has the lowest purchase cost, with a market price between $30 and $60.
It also has the lowest maintenance costs over time, as builder bushings typically last for 5+ years and are very inexpensive to replace. Their longevity and low replacement cost make them a cost-effective option for many applications.
| Feature | Johnny Joint | Heim Joint | Builder Bushing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase Cost | Highest ($70 - $130). | Moderate ($45 - $80). | Lowest ($30 - $60). |
| Maintenance Cost | Low to moderate, due to rebuildable design. | High, frequent replacements needed due to wear. | Low, lasts 5+ years, inexpensive to replace. |
| Replacement Parts | Only the polymer inner cups need replacing, saving cost. | Must replace the entire joint when it wears out. | Simple replacement of elastomer components when needed. |
Application Comparison
Johnny Joint

The Johnny joint is commonly used in off-road vehicles, especially in heavy-duty off-road and rock-crawling builds where maximum wheel travel and link angles are required. These vehicles need flexible and durable connections for control arms and track bars. Some key applications include:
- Jeep Wrangler (TJ, JK, JL series) and Jeep Cherokee (XJ): Used for heavy off-roading and rock crawling modifications that demand maximum wheel articulation and link angles.
- Off-road trucks or SUVs, such as modified Ford Bronco, Toyota Land Cruiser, Toyota Tundra/Tacoma, and Chevrolet K5 Blazer: For vehicles requiring long-travel suspension upgrades, Johnny joints are essential for high-angle flexibility.
Johnny joints are ideal for situations where extreme flex and durability are needed, especially in custom long-travel suspension builds for off-road vehicles.
Heim Joint

The Heim joint is most commonly used in motorsports, where precision control and quick feedback are critical. Some of its key uses include:
Racing applications: The precision and durability of Heim joints make them the preferred choice for motorsports that require exact control over suspension geometry.
Extreme rock crawling: While Johnny joints are generally more durable, Heim joints are used in extreme rock crawling applications, especially in vehicles demanding maximum suspension travel and uncompromising freedom of movement. For example, in extreme rock crawling modifications, stock short control arms are replaced with custom long-arm control arms, often twice as long as the original. Heim joints are used at both ends of these long arms to provide maximum angular misalignment, precise feedback, and control, along with threaded adjustment for fine-tuning suspension geometry.
Beyond off-roading, Heim joints are also widely used in other industries, including:
Builder Bushing

The builder bushing has the broadest range of applications and is used in a wide variety of industries. From vehicles to heavy equipment, builder bushings are integral in many systems. Key uses include:
- Automobiles and vehicles: They are found in suspension, steering, and drivetrain systems, where vibration dampening and slight rotational movement are required between connected components.
- Industrial machinery: They are used to reduce friction and absorb shocks in various industrial applications.
- Heavy equipment and ships: Ensuring smooth operation and durability in harsh working environments.
- Aerospace and everyday household devices: They also play a vital role in high-precision equipment and home appliances.
In the vehicle industry, whenever two components in the suspension, steering, or drivetrain systems need to connect and allow for slight twisting or provide vibration dampening, you’ll likely find builder bushings being used.
Summary
Johnny joints offer rebuildable design and high flexibility, making them ideal for off-road and heavy-duty applications. Heim joints excel in precision, often used in motorsports and extreme rock crawling. Builder bushings are best for comfort and vibration dampening, used widely in automotive and industrial applications. Understanding their differences in structure, material, function, and cost helps you choose the right part for your needs.
If you are looking to know more details about these suspension parts, check our buyers’ guide below, which will provide you both product specification information and technical articles:






